Introduction
Green hydrogen, produced using renewable energy sources like wind and solar, has emerged as a key player in global decarbonization efforts. Unlike conventional hydrogen derived from fossil fuels, green hydrogen offers a zero-emission alternative, making it crucial for industries aiming to reduce their carbon footprint. With governments and corporations investing heavily in hydrogen infrastructure, the market is witnessing rapid expansion, driven by technological advancements, policy incentives, and growing sustainability demands.
The Evolution of Green Hydrogen
Hydrogen has been a cornerstone in industrial applications for decades. However, traditional production methods, such as steam methane reforming (SMR), contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. The transition to green hydrogen began with advancements in electrolysis technology, enabling hydrogen production using water and electricity from renewable sources. Early adopters focused on pilot projects, but increasing energy demands and climate policies have accelerated large-scale adoption.
Market Trends
- Rising Government Initiatives: Subsidies, tax benefits, and hydrogen roadmaps are driving market expansion.
- Advancements in Electrolysis Technology: Improved efficiency in proton exchange membrane (PEM) and alkaline electrolyzers is reducing costs.
- Expanding Infrastructure for Transportation: Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles and refueling stations are gaining traction.
- Decentralization of Production: On-site hydrogen generation is becoming viable for industrial and commercial applications.
- Growing Role in Industrial Decarbonization: Sectors like steel, ammonia, and refining are integrating hydrogen to cut emissions.
Challenges
- High Production Costs: Electrolysis remains expensive compared to fossil-based hydrogen.
- Infrastructure Limitations: Transport and storage pose logistical hurdles.
- Energy Source Dependence: Green hydrogen’s viability hinges on renewable energy availability.
- Market Maturity: Scaling up production and creating demand remains a challenge.
Market Scope
Green hydrogen’s applications span across transportation, energy storage, industrial processing, and grid balancing. Countries like Germany, Japan, and Australia are leading innovation, while emerging markets are investing in hydrogen adoption. The market is expected to expand as partnerships between energy firms and governments drive large-scale implementation.
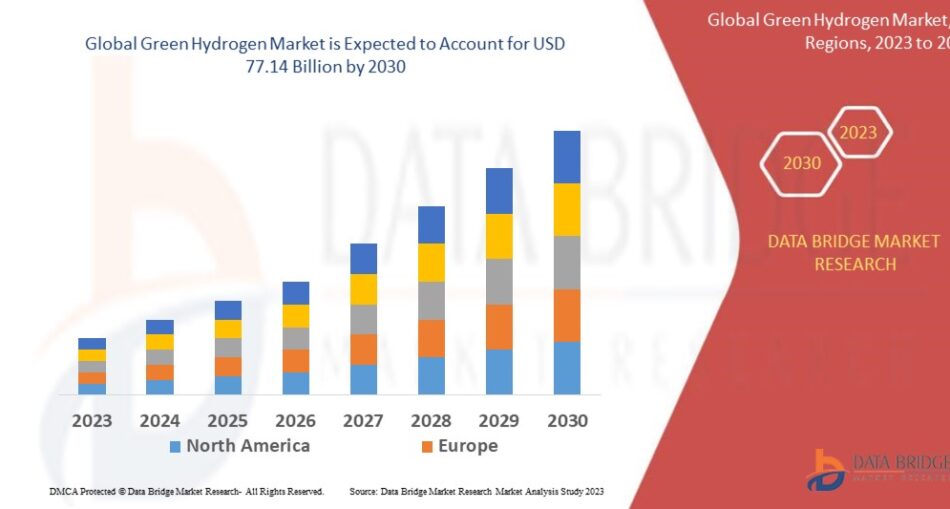
Market Size
The global green hydrogen market is projected to grow rapidly, fueled by investments in electrolyzer manufacturing and hydrogen-powered transportation. With increasing commitments to net-zero targets, market valuation is expected to surge, creating opportunities across various sectors.
Factors Driving Growth
- Strong Policy Support, with governments setting ambitious hydrogen economy targets.
- Advancements in Renewable Energy Integration, making hydrogen production more cost-effective.
- Corporate Sustainability Initiatives, accelerating green hydrogen adoption.
- Rising Industrial Demand, particularly from ammonia and steel industries.
- International Collaborations, fostering cross-border hydrogen trade.
-
The Evolution of Green Hydrogen
Though hydrogen has long been integral to industrial processes, its green counterpart is a relatively recent advancement, gaining attention alongside the growing availability of renewable energy. Initial applications centered around pilot projects and demonstration plants. However, falling renewable electricity prices, improved electrolyzer efficiency, and government-backed hydrogen roadmaps have propelled green hydrogen into commercial viability. The introduction of PEM (Proton Exchange Membrane) and solid oxide electrolyzers has enhanced system performance, marking a shift from conceptual prototypes to scalable projects across continents.
Market Trends
Government-Driven Growth: Countries like Germany, Japan, India, and Australia are investing heavily in hydrogen infrastructure. Policy frameworks, tax incentives, and strategic alliances are accelerating hydrogen adoption.
Technology Innovation in Electrolysis: Manufacturers are innovating around modular electrolyzers that enhance energy efficiency while reducing overall system costs, a key for large-scale deployments.
Hydrogen Mobility Initiatives: Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), especially in freight and public transport segments, are gaining momentum alongside the development of refueling networks.
Cross-Sector Integration: Green hydrogen is gaining a foothold in steel production, ammonia synthesis, refining, and even heating—replacing fossil-fuel-based feedstocks with zero-emission alternatives.
International Collaboration: Bilateral green hydrogen trade agreements—such as those between Australia and Japan—are fostering a global hydrogen value chain.
Challenges
Economic Feasibility: The production cost of green hydrogen remains high compared to fossil-derived hydrogen, primarily due to the capital expenditure and electricity costs associated with electrolysis.
Infrastructure Gaps: Storage, distribution, and refueling infrastructure is limited and requires significant investment to achieve scale and efficiency.
Intermittency of Renewable Energy: Green hydrogen production is dependent on consistent renewable energy supply, posing integration challenges in regions with variable generation patterns.
Regulatory and Certification Hurdles: Establishing global standards for hydrogen purity, emissions accounting, and safety protocols is essential for market maturity.
Other Trending Reports
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/middle-east-and-africa-ophthalmology-market